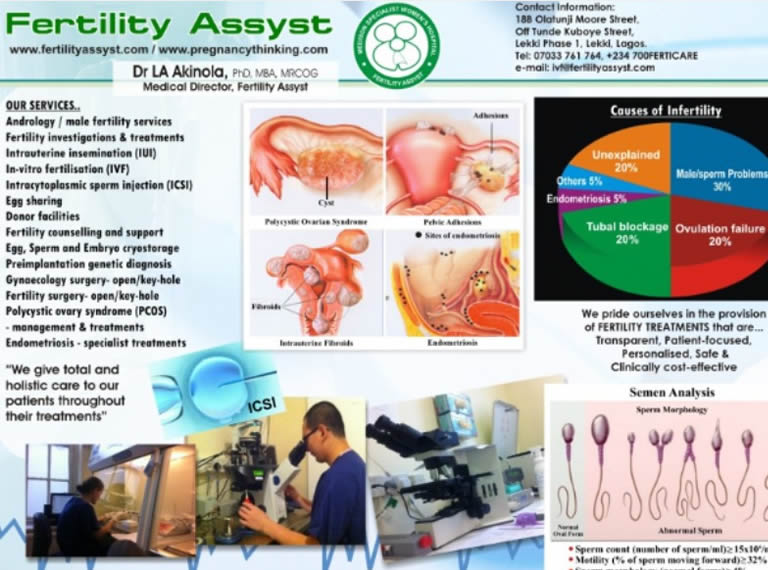
Causes of infertility
Among the infertile couples, a third of infertility causes can be attributed to the man, another third to the woman and the last third could be due to combination of factors (attributable to both sexes), undefined or unexplained and other causes like old age especially in the female, overweight/obesity or chronic medical diseases (diabetes, tuberculosis poor dieting).
Notable causes of infertility in the females includes fibroid, infections /sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia and gonorrhea for example), blocked tubes, endometriosis and in the males associated causes includes low sperm count, abnormally shaped sperm or absence of sperm in the seminal fluid. The man could also be impotent, have retrograde ejaculation or have blocked spermatic cord from past sexually transmitted infections.
Investigations
.MALE: Semen analysis will be done to exclude any cause of abnormal or low sperm count in the man (WHO, 2010). FEMALE: Ovarian reserve assessment and evidence for ovulation with blood tests are essential. Presently, serum Anti Mullerian Hormone (AMH), Prolactin and Day 21 Progesterone are measured. Other hormonal, genetic and laboratory investigations for the woman will be as required and now depend on her clinical findings and situations.
A pelvic ultrasound scans to count egg-
Assisted Reproductive techniques available in our unit
Fertility counselling and Lifestyle modifications advice given to optimize fertility issues, awareness and treatment.
Intrauterine inseminations (IUI) following ovulation induction (in women with patent fallopian tubes and men with normal sperm)
IVF and ICSI –
Freezing and storage of left over embryos for use at a later date . We also freeze-
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis, screening and PCR –
Egg and Sperm donation facilities and Gestational host and surrogacy services are offered as appropriate/indicated.
Medical Services
- Altruistic-Donor
- Donor Services
- IVF and Fertility
- Gynaecological Surgeries – Open/Key Hole
- Diagnostics
- Infertility: Treatments
- Advanced Fertility Care
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Diagnosis/Treatments
- Endometriosis Management
- Andrology and Male Fertility Services
- General and Preventive Fertility Care
- Well-man and Well-Woman
- Gynaecological Service
- Obstetrics Services
Opening Hours
Saturday: 10:00am-4:00pm
Sunday: 10:00am-1:00pm
