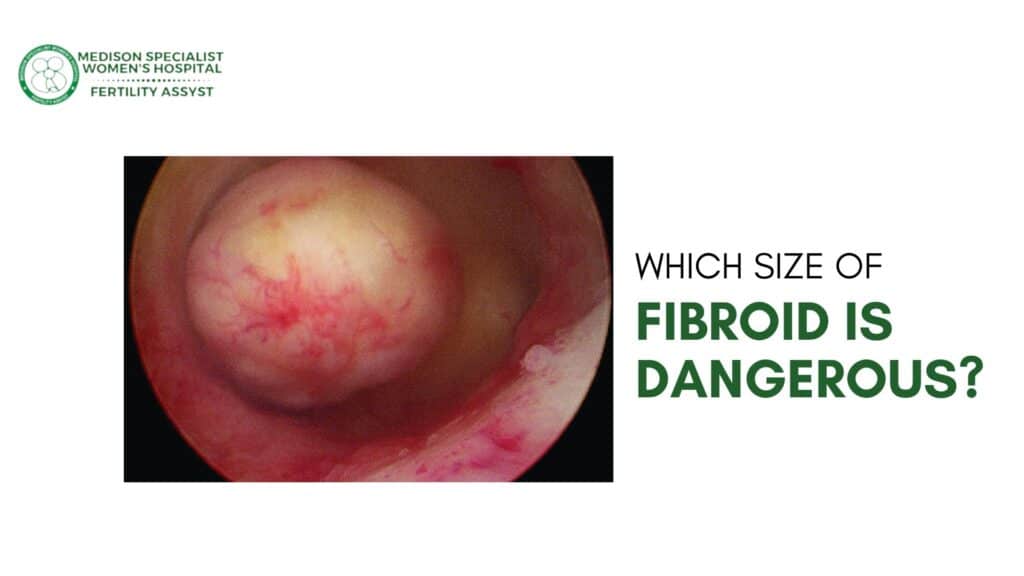
Which Size of Fibroid is Dangerous?
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are common among women of reproductive age and can vary significantly in size, number, and location. While many women experience little to no symptoms from fibroids, understanding their size and potential dangers is crucial for maintaining reproductive health.
What Are Fibroids?
Fibroids are muscular tumors that grow in the walls of the uterus. They can be as small as a pea or as large as a watermelon. The exact cause of fibroids is still unknown, but they are believed to be influenced by hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone.
Understanding Fibroid Sizes
Fibroids are classified based on their size:
- Small Fibroids: Less than 1 cm in diameter.
- Medium Fibroids: Between 1 cm and 5 cm in diameter.
- Large Fibroids: Greater than 5 cm in diameter.
Which Size of Fibroid is Dangerous?
The danger posed by fibroids is not solely determined by their size but also by their location and the symptoms they cause. Here’s a breakdown of the risks associated with different fibroid sizes:
Small Fibroids (Less than 1 cm):
Generally, small fibroids are less likely to cause significant health issues or symptoms. However, if they are located in a critical area, they can still lead to complications such as pain or discomfort.
Medium Fibroids (1 cm – 5 cm):
Medium-sized fibroids may start to cause more noticeable symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on surrounding organs. While they are not typically considered dangerous, their symptoms can impact a woman’s quality of life.
Large Fibroids (Greater than 5 cm):
Large fibroids are more likely to cause severe symptoms and complications. They can lead to significant discomfort, heavy bleeding, and even anemia due to blood loss. Additionally, large fibroids can interfere with fertility and may increase the risk of miscarriage or preterm labor.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional:
- Severe pelvic pain or pressure
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pain during intercourse
- Changes in urinary or bowel habits
- Difficulty conceiving
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis typically involves a pelvic exam, ultrasound, or MRI to determine the size, number, and location of fibroids. Treatment options vary based on the size of the fibroids and the severity of symptoms, including:
- Medication: Hormonal treatments to help manage symptoms.
- Non-invasive procedures: MRI-guided focused ultrasound therapy.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Uterine artery embolization or laparoscopic myomectomy.
- Surgery: Hysterectomy for women with severe symptoms or complications.
Conclusion
Understanding fibroids’ size and potential dangers is essential for women’s health. While small fibroids may pose minimal risk, medium and large fibroids can lead to significant complications. If you suspect you have fibroids or are experiencing concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
For more information on fibroids and women’s health, contact The Medison Hospital.